SparseSat-NeRF: Dense Depth Supervised Neural Radiance Fields for Sparse Satellite Images
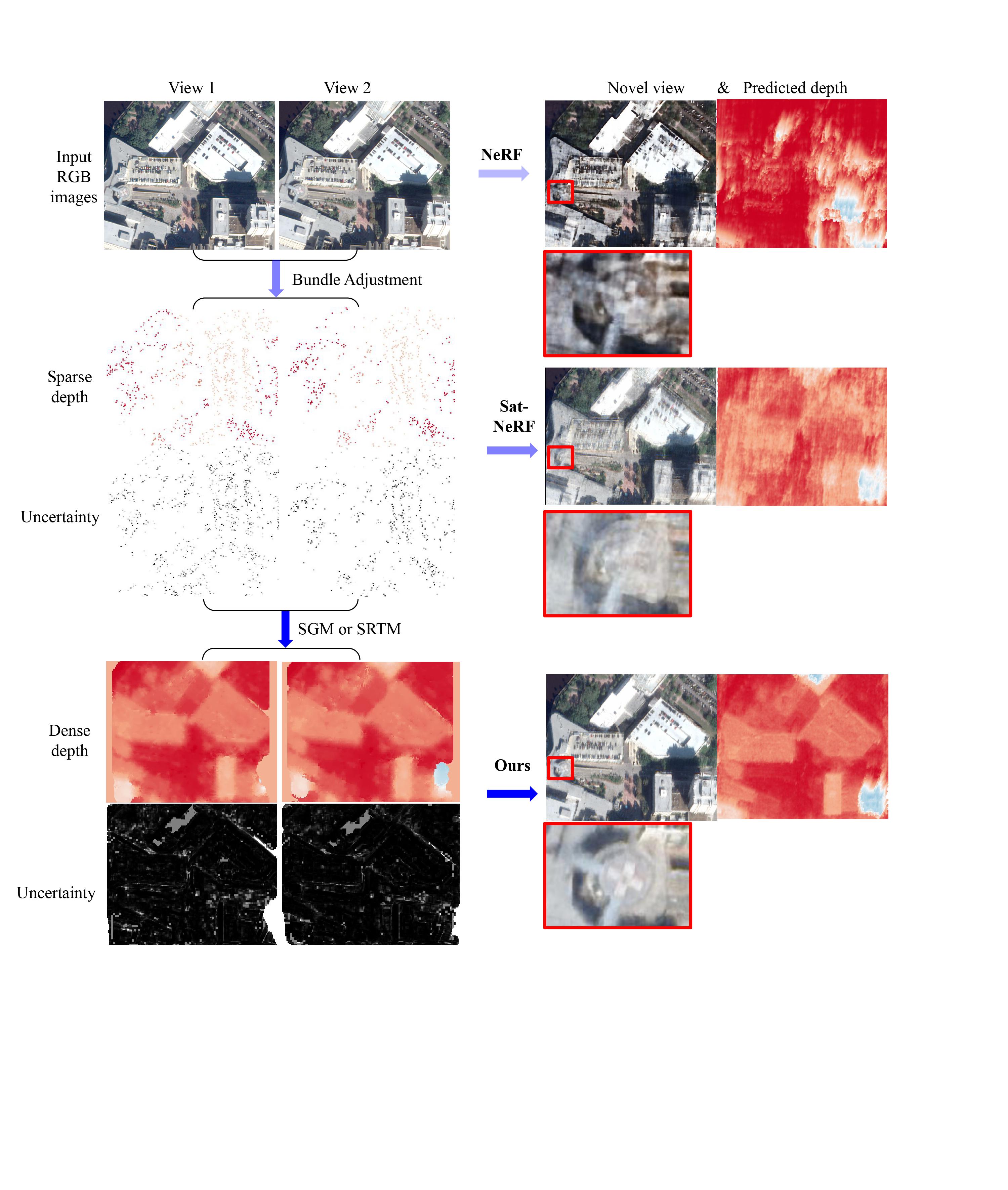
Figure. Workflows of SS-NeRF (Ours), Sat-NeRF and NeRF. In our experimental setting we use 2 or 3 satellite images to optimize the neural radiance fields for photo-realistic novel view rendering, and for DSM recovery. Without any depth supervision, NeRF fails to render high quality novel views and DSM. Sat-NeRF incorporates sparse depth information and uses the bundle adjustment re-projection errors as uncertainties to weigh the depth loss; it improves the results, but the artifact remain present due to the insufficient $#$ of training views. SS-NeRF further employs low resolution dense depth maps from traditional methods such as SGM, and uses the $\left(1 - correlation \right)$ score as uncertainty, and takes advantage of the dense depth to guide sampling along the casted ray, leading to improved performance.
Abstract
Digital surface model generation using traditional multi-view stereo matching (MVS) performs poorly over non-Lambertian surfaces, with asynchronous acquisitions, or at discontinuities. Neural radiance fields (NeRF) offer a new paradigm for reconstructing surface geometries using continuous volumetric representation. NeRF is self-supervised, does not require ground truth geometry for training, and provides an elegant way to include in its representation physical parameters about the scene, thus potentially remedying the challenging scenarios where MVS fails. However, NeRF and its variants require many views to produce convincing scene’s geometries which in earth observation satellite imaging is rare. In this paper we present SparseSat-NeRF (SS-NeRF) - an extension of Sat-NeRF adapted to sparse satellite views. SS-NeRF employs dense depth supervision guided by cross-correlation similarity metric provided by traditional semi-global MVS matching. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on stereo and tri-stereo Pléiades 1B/WorldView-3 images, and compare against NeRF and Sat-NeRF.
Code
BibTeX Citation
@article{zhang2023ssnerf,
author = {Lulin Zhang and Ewelina Rupnik},
title = {SparseSat-NeRF: Dense Depth Supervised Neural Radiance Fields for Sparse Satellite Images},
journal = {ISPRS Annals},
year = {2023}
}
